Modern Farming – Definition, Types, Importance & advantages

According to most surveys, food demand is expected to increase by 25% by 2030, while it is expected to increase to 70% by 2050. Modern farming is the best way to meet the food demand of all.
The concept of modern farming was introduced in rice in the mid-1950s. But traditional farming is still practiced in most of the backward areas or in rural India that do not know about modern agriculture, technology, science. In contrast, Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh were the first states to prioritize modern farming and over time have been increasing the use of modern techniques, experiments, and science.
What is Modern Farming

The term “modern farming” refers to the application of modern technology, practices, and science to increase agricultural output. Farming is the cultivation of crops, plants, domestic animals, fish, birds, and other items for food, fabric, and other amenities of life. Farming is critical to the advancement of human civilization. Prior to the industrial revolution, the vast majority of the people relied on farming for their daily necessities such as food, clothes, and shelter. They had little concept of the global marketplace and used to produce relatively little owing to the usage of Modern farming or organic farming practices. But things have changed since then.
Farmers understand the modernity of agricultural systems, but it is difficult to convey with specificity. Nonetheless, the contrasts between modern and traditional agriculture systems have serious repercussions for the future evolution of the global food system, despite the fact that few, if any, systems fit fully into either category.
Traditional methods: The way farmers view themselves and their jobs is perhaps the most significant distinction between the groups. Traditional farmers, for example, frequently state that they strive to operate efficiently with the resources at hand.
That is, they make use of the land, power sources, rainfall, seeds, tillage methods available to them to create what nature provides. Traditional methods are used to cultivate the land, select and plant seeds, protect plants from competing plants and animals, and harvest the harvest. Surplus items are sold at adjacent stores. These producers typically report having limited capacity to modify these processes and some actively want to prevent change.
The production of such systems is largely determined by the inherent fertility of the soils, which is improved by skilled management, and by the climate. The technological and management systems involved are frequently distinguished by a lack of access to, or a reluctance to utilize, new information regarding production and/or management, as well as governmental or commercial help. Their productivity grows slowly, typically in reaction to external events that lessen producer isolation, enhance market access, or encourage investment in water and land.
Modern farming: In modern agricultural systems, farmers think they have much more central responsibilities and are willing to use technology and information to manage most components of the system, which is quite different from traditional farmers’ perspective. In contrast to the isolation inherent in old arrangements, Modern agriculture views success as being dependent on linkages—access to resources, technology, management, investment, markets, and supporting government policies.
As a result, much of the success of modern systems is dependent on the development and Soil fertility is maintained by providing particular nutrients when they are low.; the use of Machine power and technology are used to produce the soil conditions required to encourage plant development while causing the least amount of disruption and soil loss.; the use of improved genetics for crops and livestock to improve yields, quality, and reliability; and the use of modern genetic and other techniques to protect the environment.
This success is also dependent on having access to efficient, effective irrigation to augment rainfall in various regions, as well as improved harvesting, handling, and storage equipment and procedures to avoid losses and effectively sell goods. In turn, it is dependent on both public and private investment to offer access to technology, equipment, information, and physical facilities across the production marketing system.
Modern agriculture in developed countries, including the United States, entails far more than farms and farmers; it is dependent on massive, highly sophisticated systems that move, store, and process producers’ output across a vast value chain that includes food products and final consumers.
Modern Methods Of Farming
Aside from the farming techniques listed above, additional ways are used in different parts of India. Many of these do not fall under the purview of traditional farming methods in India. This includes the following:
Aeroponics System
Aeroponics is the method of growing plants in the air or mist without the need of soil. It is a subtype of hydroponics that works by suspending the plant root in the air. Farmers will have more control over the quantity of water they consume if they employ this approach.
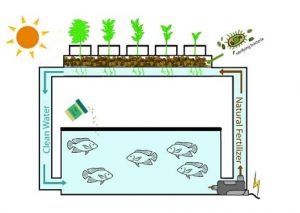
Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a closed-loop system that depends heavily on fertilization from the symbiotic link between aquaculture and agriculture. This agricultural technique combines traditional aquaculture with hydroponics.
Hydroponics
The hydroponics method is a dirt-less farming approach that does not use any sort of soil. The technique entails growing healthy plants without the need of solid media by employing nutrients such as mineral-rich water solutions. Hydroculture is a subset of hydroponic farming, and the nutrients utilized in hydroponic farming systems come from many sources.
Monoculture
This approach involves the cultivation of a single crop in a specified farming region. However, in a nation like India, the Monoculture farming practice is not frequently used. Indoor farming, such as producing medicinal plants, falls under the category of monoculture. Monoculture is a modern agricultural method in which a single crop or plant is cultivated.
Importance of Modern Agriculture
Because of the more food that modern systems supply, hundreds of millions of individuals have been able to achieve more of their potential.
Better lives, therefore increasing the accomplishments of everybody, from kids to seniors It boosts workforce productivity and generally promotes human development and progress. The current levels of hunger and malnutrition, which affect one billion people, are the result of inadequate policies, low productivity, and low earnings. Failure to continue to use innovative technology to increase productivity on the farm and across the food system exacerbates all aspects of these issues, particularly those imposed on low-income persons and families.
Physical environmental constraints, which have become more significant public issues, have been substantially alleviated by modern agriculture, which has reduced:
The need to increase land area, reducing pressure to farm vulnerable lands and wooded regions. Modern agriculture incorporates successful new technologies, such as biotechnology, to permit increased yields while reducing the environmental effects. This reduces the amount of land, fertilizer, and pesticides used per unit of yield.
Advances in processing technology and handling contribute significantly to enhanced food safety through pathogen reductions and significant reductions in post-harvest losses, which boost food supply.
Consumers gain enormously from modern agriculture, both economically and socially.
Increased quality of life and living standards as food prices fall. This effectively improves consumer earnings since it frees up more purchasing power for other consumer products such as education, health care, leisure, and so on.
Modern agriculture contributes to global political stability by increasing food availability, improving food quality, and making it more accessible to more people.
Traditional Agriculture Vs Modern Agriculture.
Advantages of Modern Agriculture
- It has the potential to reduce production time.
- Increase the price and quantity of the products.
- Sophisticated farming employs modern storage technologies that decrease food grain waste.
- It is used to water the crops elegantly.
- Modern equipment can reduce farmers’ efforts.
- Increases the soil’s fertility.
- Crop protection is an important aspect of modern farming.
- Reduce the impact on the environment.
- Machines are useful for seed sowing.
- The usage of HYV seeds has greatly enhanced productivity.