Overview of Aquaponics Systems & Farming
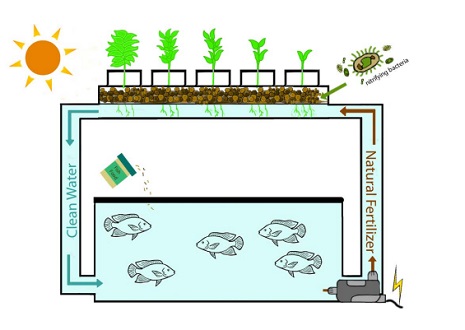
Natural resource scarcity is forcing us to consider more environmentally friendly ways of life. Aquaponics is a growing sustainable food production method that combines aquaculture and horticulture in a circular system that mimics natural nutrient and water cycles. Aquaponics methodology has gained increased interest in recent years, and the number of aquaponic practitioners has increased significantly since 2008.
Aquaponic is a part of modern farming technology that is a subset of the larger discipline of integrated agri-aquaculture systems, which seeks to combine animal and plant culture technologies to confer benefits and conserve nutrients and other biological and economic resources. It merged in the early 1970s in the United States and has recently seen a resurgence, particularly in Europe.
Aquaponic employs several principles, including, but not limited to, efficient water use, efficient nutrient use, reduced or eliminated environmental impact, and the use of biological and ecological approaches to agricultural fish and plant production. Water sources are critical for ensuring that the nutrients required for fish and plant production are available and balanced, and system water chemistry is critical for optimizing fish and plant production.
What is Aquaponics?
Aquaponics is a sustainable food production method that combines aquaculture (raising aquatic animals) and hydroponics (cultivating plants in water).

Both terrestrial plant and aquatic animal production systems, in essence, share a common resource: water. Plants consume water through transpiration and release it into the surrounding gaseous environment, whereas fish consume less water, but their contained culture produces significant wastewater streams due to accumulated metabolic wastes.
Aquaponic is useful for anyone who wants to grow food, and it can be done almost anywhere there is clean water and electricity.
Aquaponics is frequently heralded as the food-production technology of the future. Aquaponic Systems are said to use only 2 to 10% of the water required in traditional vegetable or crop production and have the potential to produce 10 times the output while avoiding the use of harmful chemicals, pesticides, and other chemicals.
The most significant component of Aquaponics is the little amount of land/space required, resulting in what is known as Urban Aquaponics/ Urban Agriculture/ Urban Farming/ Urban Gardening/ Terrace Gardening/ Vertical Gardening/ Office Farm (indoor), and so on.
Because it is very efficient, natural resource usage is relatively limited, resulting in the conservation of valuable natural resources like water, land, and the environment.
Aquaponics Systems
Aquaponics is divided into two parts: aquaculture (raising aquatic animals) and hydroponics (growing plants). Plant support material like gravel or sand that also works as bio-filter media can be used to integrate the bio-filter and hydroponic components.
However, aquaponics systems nowadays often employ electrical energy and are fairly difficult to put together. As a result, this idea addresses the issue by creating an aquaponics system that is driven by solar energy and is simple to put together. An electrical water valve, a water pump, and a solar energy supply comprise this aquaponics system.
The majority of Malaysia’s energy comes from oil. Because the globe consumes energy sources, a preventative measure to safeguard the environment must have been taken. Renewable energy is an excellent substitute for traditional energy sources. Malaysia is an ideal location for solar panel energy generation due to its proximity to the equator, which receives an average of 12 hours of sunlight each day and night throughout the year.
As a result of the project’s location, the solar panel is the optimal green energy source for powering the aquaponics control pump. The primary goals, however, are to power the water pump and air pump with green energy using solar panels. Because the water pump required alternating current voltage, an inverter was employed in this application. Instead of replacing the AC water pump with a DC water pump, this idea focuses on using an inverter.
Types of Aquaponics Systems
Aquaponics has three basic growth methods: Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Ebb & Flow, and Raft or Deep Water Culture (DWC).
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Aquaponics Systems
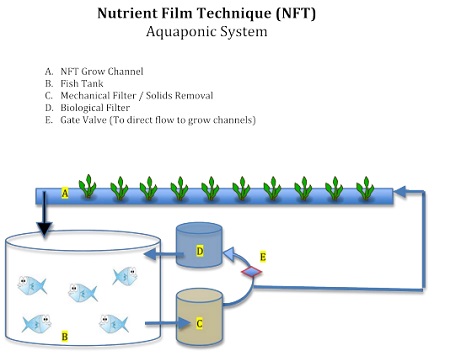
The Nutrient Film Technology (NFT) is the most widely utilized hydroponic technique and is easily adapted for use in Aquaponics. A thin layer of water containing dissolved nutrients from the fish tank is pushed into the bare roots of the plants in a watertight gully or channel using this approach. The re-circulating stream’s depth is quite modest, providing an adequate supply of oxygen to reach the plant roots. The primary benefit of the NFT system is that the plant roots are constantly supplied with water, oxygen, and nutrients. The disadvantage of NFT is that it has less buffering against disruptions in the flow, such as power outages, but it is a very productive technology overall.
Ebb and Flow / Grow Bed Aquaponics Systems
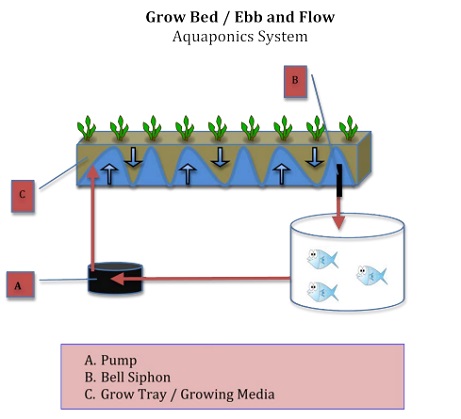
Ebb and Flow Aquaponics is another popular approach among home producers. The growth area is a large, deep container with plenty of surface space. This container is filled with gravel, LECA, or similar soil-free growth media where the veggies will be grown.
Planting is possible. An adjustable timer controls the water pump, circulating water to fill the tub in an “ebb-and-flow” fashion. The grow bed becomes saturated with water while the pump operates. When the pump is turned off, the water gently drains back into the fish reservoir. Oxygen is drawn through the roots as it drains. A bell siphon is an alternative method of supplying water in an ebb-and-flow way. A siphon is a device that moves water from a higher to a lower container. In an aquaponics arrangement, siphons may be modified to regulate the flooding and draining of grow beds. In this context, they are referred to as auto siphons, which are siphons that can start and stop in response to changing water levels. Bell siphons and loop siphons, in particular, are two useful and widely used techniques for this application. Bell siphons are also useful in biological filters.
Make a wet/dry environment that is favorable to aerobic nitrifying bacteria.
Raft or Deep Water Culture (DWC) Aquaponics Systems
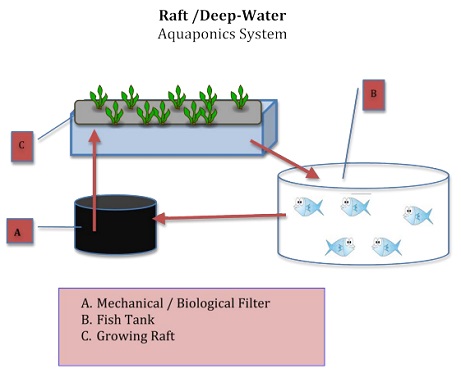
The most common technology for large-scale commercial Aquaponics is raft or deep water culture (DWC). Plants are cultivated on perforated rafts, which float in specialized water tanks and are often constructed of Styrofoam or a similar buoyant material. Plant roots are frequently exposed and submerged in water. This is a very productive approach that needs strong aeration and extensive filtration to keep the water pure and free of solid trash.
List of Aquaponics Materials
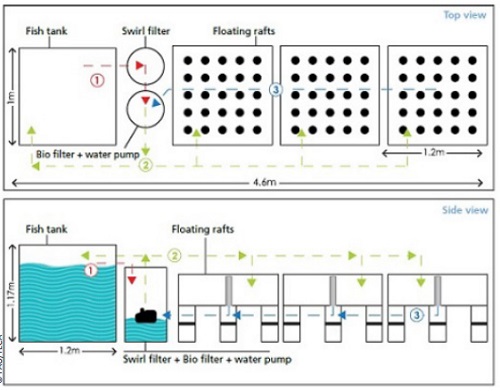
A plot of land measuring 0.5 acres (2000 square meters) would be excellent for creating a small-scale aquaponics unit to be managed commercially. It would mainly consist of one rectangle fish tank, ten plant grow-beds, as well as a Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) and Filtration Units, Pumps, Aerators, and so on. The estimated initial cost is Rs.3.7 lakh, with operational expenditures of Rs.4.1 lakh (total Rs. 7.8 lakh). The technical specifications, design, and layout, anticipated project costs, and estimated project are as follows:
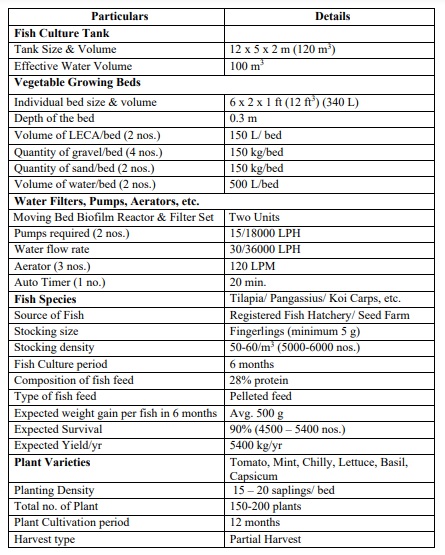
Aquaponics Design
Besic Aquaponics Design
Crops Grown in Aquaponic Systems
Aquaponics can be used to grow a wide range of plants. Here are a few examples of plants that have thrived in Aquaponics:
Green leaf lettuce, red leaf lettuce, and other leafy lettuces
- ‘Bok Choi’
- Chard (Swiss)
- Arugula
- Basil
- Mint
- Watercress
- Chives
- Microgreens
Fruits Grown in Aquaponic Systems
Some fruiting plants may have greater nutritional requirements and, as a result, will thrive in densely stocked, well-established systems. To stimulate blooming, we recommend adding potassium sulfate (potash sulfate) to your water.
These are some examples:
- Tomatoes
- Peppers
- Cucumbers
- Beans
- Peas
- Squash
The Best Aquaponics Fish
Aquaponic systems may be used to grow a broad range of fish and other aquatic creatures. Freshwater, herbivorous, or omnivorous fish are excellent alternatives due to their long-term viability, simplicity of feeding, and effective feed conversion. Here are our top five fish picks:
- Tilapia
- Catfish
- Koi
- The goldfish
- The tropical
- Tropical Fishes
Other fish to consider include:
- Pacu’s
- ‘Trout’
- Crappie’s
- Barramundi
- Perch, silver
- Golden eagle
- Perch (yellow)
- Prawns from freshwater
- The crayfish
Advantages of Aquaponic Farming
According to FAO, there are several advantages to using a system design, such as aquaponics to raise food. So, what are the advantages of aquaponics?
- Aquaponics is a very efficient water-saving method. Nelson and Pade claim that aquaponics requires just 1/6th the water of typical agriculture while producing 8 times more food per acre.
- Because aquaponics does not require soil, it is immune to soil-borne infections.
- Aquaponics does not necessitate the use of fertilizers or chemical pesticides.
- Aquaponics is synonymous with better yields and higher quality produces.
- Aquaponics provides more biosecurity and fewer threats from outside pollutants.
- Aquaponics may be employed on non-arable terrain like deserts, deteriorated soil, or salty, sandy islands.
- Because it mirrors nature’s cyclical method, aquaponics produces less waste.
- Aquaponics necessitates everyday duties like harvesting and planting, which are labor-saving and hence suitable for people of all genders and ages.
- Aquaponics may be used to combine livelihood options for landless and impoverished households in order to secure food and modest revenues.
- Aquaponics produces fish protein, which is a useful complement to many people’s diets.
Disadvantages of Aquaponic Farming
There are two sides to every coin. And, once again, according to the FAO analysis, there are certain drawbacks to using an aquaponics system. So, what are the flaws of aquaponics?
- One of the aquaponics’ disadvantages is its extremely expensive initial start-up expenses (compared to both hydroponics and soil production methods).
- Aquaponics necessitates extensive knowledge of the natural world. Farmers must understand not just how to cultivate crops but also how fish and bacteria function in order to be successful. In addition, technical expertise in plumbing or electrical is required.
- As a follow-up to the preceding point, it is sometimes difficult to establish a perfect match between the demands of fish and plants (such as pH, temperature, and substrate);
- Compared to stand-alone aquaculture or hydroponics, aquaponics offers fewer management alternatives (a problem that has arisen); 5. Mistakes in maintaining the system can swiftly cause its collapse;
- Daily management is required, implying that structure is critical.
- It is an energy demand, which implies that it has energy expenses.
- Fish feed must be obtained on a regular basis;
- Aquaponics goods alone are insufficient to maintain a balanced diet;
Furthermore, a good aquaponics system must have excellent organic solid filtration – which is the role of bacteria or algae. Over two-thirds of aquaponics system failures are caused by inefficient solid waste management.








